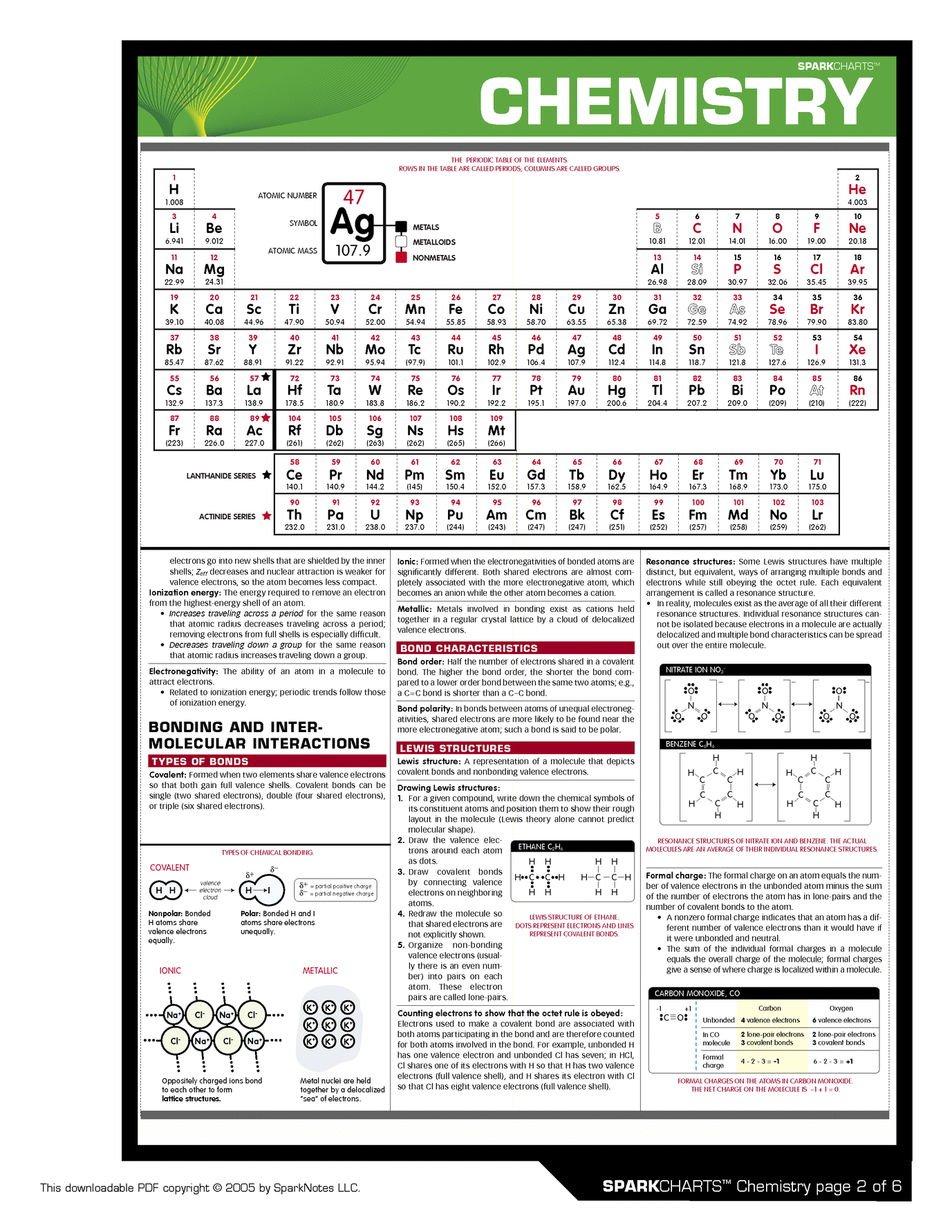
Cellular Respiration Process In Order

It includes glycolysis, the tca cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Cellular respiration process in order. And by laundromat, i mean your body! Glycolysis, the citric acid cycle (the kreb's cycle ), and electron transport. It is the process in which the oxidation of the carbohydrate molecule, glucose, takes place in the presence of oxygen.
Here are three important steps of cellular respiration. The final two steps together comprise aerobic respiration. But this is all cellular respiration is.
Cellular respiration can be summarized as glucose + oxygen= carbon dioxide + water + atp (energy) cellular respiration in plants. And the reality is, depending on the efficiency of the cell in performing cellular respiration, it'll probably be more on the order of 29 to 30 atps. This essential process happens in the cytosol of the cytoplasm.
Steps of cellular respiration 1 (glycolysis): Aerobic cellular respiration refers to the process by which living organisms convert nutrients into energy for the body to use via the oxidization of nutrients. Glycolysis can occur with or without oxygen.
It's is a very fast process; Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces atp. During aerobic respiration, catabolic reactions convert larger complex organic molecules into atp, the chemical that drives most physiological processes in the body.in other words, respiration is the key way that a cell gets chemical.
Every machine needs specific parts and fuel in order to function. Extracting those nutrients necessary to keep us going and then converting them into useable energy is the job of our cells.this complex yet efficient metabolic process, called cellular respiration, converts the energy derived from sugars, carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into adenosine triphosphate, or atp, a high. Usually, this process uses oxygen, and is called aerobic respiration.it has four stages known as glycolysis, link reaction, the krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain.